The rapid expansion of the internet and social media platforms has transformed how people connect, share, and consume content. While this digital revolution has unlocked unprecedented opportunities for communication and innovation, it has also led to significant environmental challenges. Understanding the complex relationship between online activities, data storage, and resource consumption is essential to mitigate the negative effects on the planet. This article explores the hidden environmental costs of our digital habits and highlights emerging trends aimed at promoting a more eco-friendly online ecosystem.
Digital Infrastructure and Energy Consumption
Every email sent, video streamed, and social media post uploaded travels through a vast network of servers, routers, and data centers. This global infrastructure requires enormous amounts of electricity to operate and cool down the hardware that powers our digital lives.
Data Centers as Energy Hubs
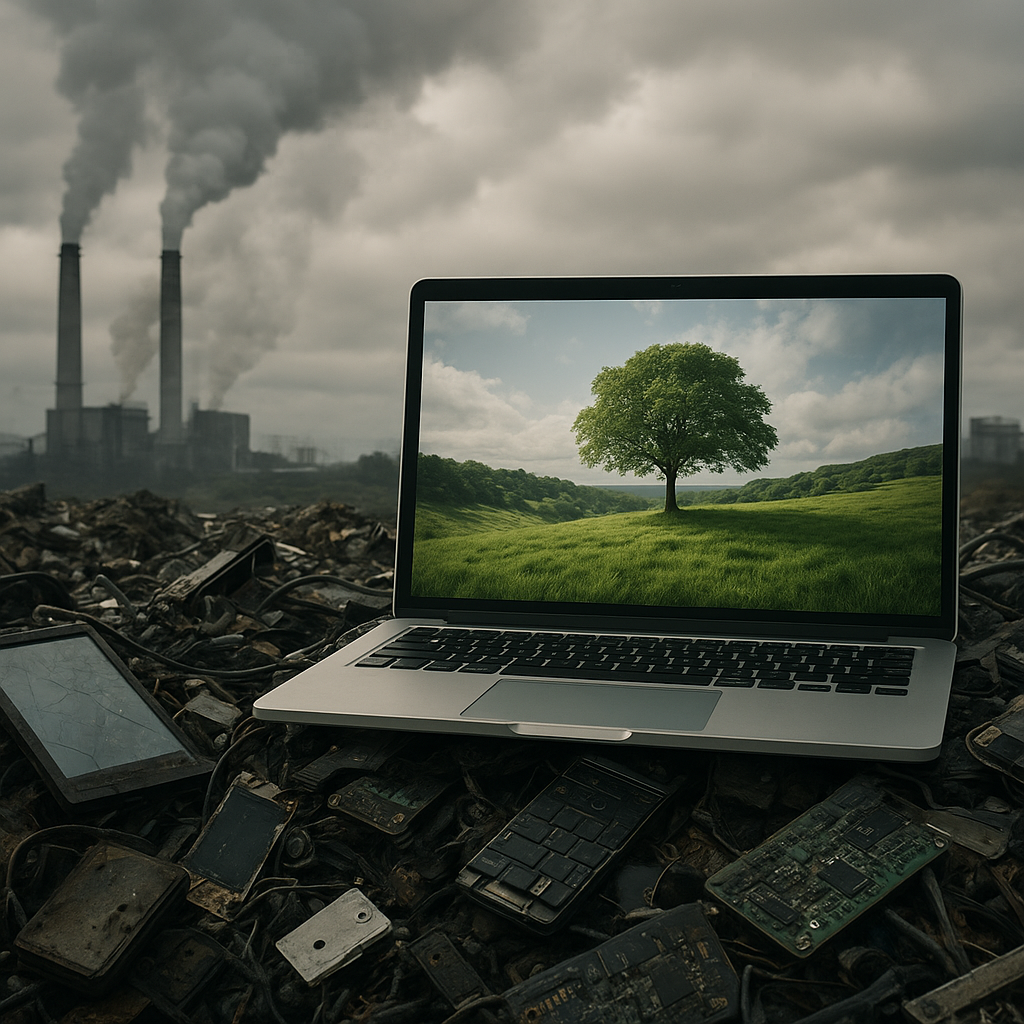
Data centers are the backbone of the digital world. Housing tens of thousands of servers in climate-controlled environments, they consume a staggering share of the world’s electricity. To maintain optimal performance, each data center is equipped with sophisticated air conditioning and cooling systems, which can account for nearly 40% of total energy usage. As demand for cloud services, streaming platforms, and social media continues to skyrocket, data centers are under pressure to expand capacity, often leading to higher emissions.
Power Sources and Grid Dependence
Many data centers still rely on fossil-fuel-generated electricity, particularly in regions where renewable options are limited or more costly. The carbon footprint of a single data center can rival that of a small city. Transitioning to clean energy sources is critical, but challenges such as grid stability, geographic constraints, and initial investment hurdles can slow adoption.
Efficiency Through Innovation
Advancements in server design, cooling technology, and facility management have led to improved energy efficiency. Techniques such as liquid cooling, free-air cooling in colder climates, and the use of AI-driven energy management systems help reduce power consumption. Nevertheless, the overall environmental impact remains substantial as usage continues to grow.
Social Media and Data Footprints
Social media platforms are not only communication channels but also massive repositories of user-generated content. Every image, comment, and like contributes to the ever-growing digital footprint stored in data centers worldwide.
Content Proliferation and Storage Demands
The average social media user uploads hundreds of photos and videos per year. Platforms replicate this content across multiple servers to ensure availability and quick access, multiplying storage needs. This replication, while beneficial for performance and reliability, leads to increasing resource use and a larger footprint.
Streaming and Real-Time Interactions
Live streaming and real-time video calls are among the most bandwidth-intensive activities on the internet. Popular live streams can attract millions of viewers simultaneously, requiring substantial network bandwidth and server capacity. This surge in data transfer directly correlates with higher energy consumption across content delivery networks (CDNs).
- Video conferencing tools
- Live events and webinars
- Interactive social features
Algorithmic Impacts
Recommendation algorithms drive higher engagement but also encourage more time spent online, increasing energy usage. While these algorithms improve user experience, they indirectly elevate the carbon footprint of digital platforms by demanding more server cycles and network traffic.
Trends in Sustainable Technology
The tech industry is responding to environmental concerns by investing in innovation that reduces the ecological impact of digital services. From hardware design to data center operations, sustainability has become a focal point of research and development.
Renewable Energy Integration
Major tech companies are signing power purchase agreements (PPAs) to secure renewable energy for their operations. Solar farms, wind turbines, and hydroelectric projects are increasingly used to power data centers. Some organizations even aim for carbon-neutral or carbon-negative operations by investing in carbon offset initiatives and forest conservation programs.
Green Hardware and Lifecycle Management
Manufacturers are designing servers and networking equipment with a focus on recyclability and modularity. By extending the lifespan of hardware and facilitating repair or component replacement, companies can reduce electronic waste and resource extraction. Responsible disposal and recycling programs ensure that end-of-life equipment is processed in an eco-friendly manner.
Software Optimization and Virtualization
Software engineers are optimizing code to run more efficiently, reducing the computational power required for common tasks. Containerization and virtualization techniques allow multiple applications to share the same hardware resources, improving utilization rates. This consolidation leads to fewer physical servers being needed for the same workload, cutting down on electricity and cooling demands.
Consumer Responsibility and Behavioral Change
Individual actions play a crucial role in shaping the environmental footprint of the digital world. Users can adopt simple habits and preferences that encourage platforms and service providers to prioritize sustainability.
Mindful Content Consumption
Reducing video quality when high definition is unnecessary, clearing cache regularly, and unsubscribing from unused cloud storage services are small steps that aggregate into significant energy savings. Opting for text-based news or podcasts over streaming videos can also lower data usage.
Support for Eco-Friendly Platforms
Choosing social networks and cloud services that commit to green energy and transparent environmental reporting sends a market signal to the entire industry. By favoring companies with strong sustainability practices, consumers can drive broader change.
Advocacy and Education
Raising awareness about the environmental costs of digital habits is essential. Social media advocacy campaigns, online workshops, and collaborative projects can educate communities about best practices. As more people become informed, collective pressure on policymakers and corporations increases, leading to stronger regulation and industry-wide commitments.
Future Outlook: Balancing Growth with Ecology
The digital world is set to expand further with the advent of technologies like 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence. Each advancement promises benefits but also brings new environmental challenges. Striking a balance between innovation and sustainability will require collaboration across sectors:
- Governments enacting policies that incentivize renewable energy adoption.
- Tech companies investing in carbon-offset projects and green certifications.
- Researchers developing more efficient hardware and software solutions.
- Consumers embracing responsible online behavior and supporting eco-friendly services.
Only through coordinated efforts can the digital revolution continue to thrive without sacrificing the health of our planet. Recognizing the hidden costs behind our screens is the first step toward creating a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable online future.